Technology
Analysis of Nigeria’s Renewable Energy Sector: Opportunities and Challenges
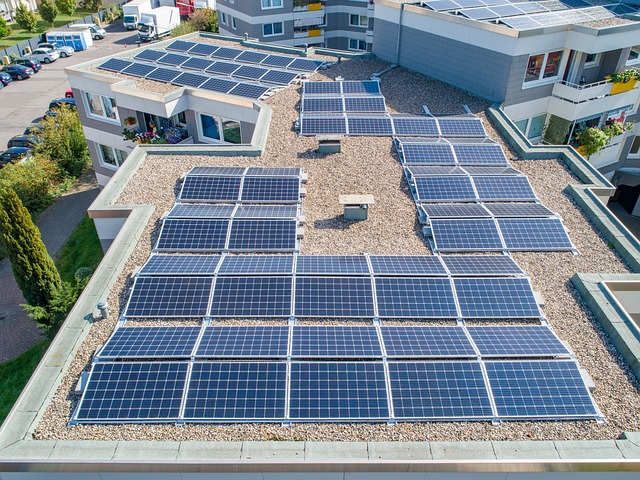

Nigeria, as Africa’s most populous nation and largest economy, faces significant energy challenges due to its heavy reliance on fossil fuels. However, the country possesses immense potential for renewable energy resources, it has an exciting future ahead, like gamers on 22bet.
Renewable Energy Potential
Nigeria is blessed with abundant renewable energy resources. Solar energy potential is high throughout the country, with an average of 5.3 kWh/m² of daily solar radiation. Wind resources are particularly favorable in the northern regions, with wind speeds ranging from 2 to 6 meters per second. The country also possesses substantial hydroelectric potential, thanks to its numerous rivers and water bodies. Additionally, biomass resources are plentiful, making them a viable option for energy production.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The Nigerian government has recognized the importance of renewable energy and implemented several policies and initiatives to promote its adoption. The National Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Policy (NREEEP) and the Renewable Energy Master Plan (REMP) provide frameworks for renewable energy development. The government also offers incentives such as tax breaks, import duty waivers, and grants to attract private sector investment. Furthermore, the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) aims to extend electricity access through renewable energy solutions, particularly in rural areas.
Market and Investment Landscape
Nigeria’s renewable energy market is ripe with investment opportunities. The private sector has shown increasing interest, with local and international companies investing in solar, wind, and hydro projects. The Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) has implemented feed-in tariff regulations to provide stability and attract private investments. Additionally, partnerships with international organizations, such as the World Bank and African Development Bank, have facilitated funding and technical support for renewable energy projects.
However, several challenges persist. Limited access to financing remains a major obstacle, as high upfront costs deter potential investors. Inadequate infrastructure, including grid constraints and transmission losses, hampers effective integration of renewable energy into the existing system. Additionally, policy implementation and regulatory frameworks require further streamlining to encourage investor confidence.
Socioeconomic and Environmental Impacts
The adoption of renewable energy in Nigeria has significant socioeconomic and environmental benefits. It can contribute to job creation, especially in rural areas, through the establishment of renewable energy projects and local manufacturing of renewable energy equipment. Additionally, it can improve energy access, particularly in underserved regions, leading to enhanced educational opportunities, healthcare services, and economic development.
From an environmental standpoint, increased renewable energy deployment can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change impacts. Moreover, it can alleviate the negative health effects associated with fossil fuel combustion, such as air pollution and respiratory illnesses.
Opportunities in Renewable Energy
The abundant renewable energy resources in Nigeria present numerous opportunities for the country’s energy sector. Solar energy, with its year-round availability, can be harnessed through large-scale solar farms and distributed solar systems to meet both urban and rural energy needs. Wind power, especially in the northern regions, can be tapped for electricity generation and contribute to the diversification of the energy mix. Nigeria’s vast hydroelectric potential can be further developed, leveraging its rivers and water bodies to expand clean energy production.
Furthermore, biomass resources, such as agricultural waste and forestry residues, can be utilized to generate electricity and provide thermal energy for cooking and heating. This not only promotes rural electrification but also reduces dependence on traditional biomass fuels like firewood and charcoal, leading to improved indoor air quality and reduced deforestation.
Integration with the Grid and Energy Storage
Integrating renewable energy into Nigeria’s existing energy grid is crucial for its successful deployment. The variability of solar and wind resources necessitates grid infrastructure upgrades and investments in energy storage systems. By implementing smart grid technologies, energy management systems, and grid-scale battery storage, the intermittent nature of renewable energy can be mitigated, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
Furthermore, decentralized energy systems and microgrids can enhance energy access in remote areas, reducing transmission losses and enhancing overall system efficiency. These systems can empower local communities, stimulating economic activities and fostering energy independence.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Despite the opportunities, Nigeria faces significant challenges in realizing the full potential of its renewable energy sector. Limited access to financing is a significant barrier, as high upfront costs and perceived risks deter potential investors. To address this, the government should collaborate with financial institutions to develop innovative financing models, such as green bonds and venture capital funds, tailored to the renewable energy sector.
Additionally, inadequate grid infrastructure and transmission capacity pose challenges to the integration of renewable energy. Investments in grid expansion, smart grid technologies, and transmission infrastructure upgrades are crucial to facilitate the smooth integration of renewables into the existing system.
Furthermore, policy implementation and regulatory frameworks need strengthening to provide a stable and predictable business environment. Streamlining licensing procedures, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and ensuring transparency in the regulatory process will enhance investor confidence and attract more private sector participation.
Nigeria’s renewable energy sector holds immense potential for sustainable development, energy security, and climate change mitigation. Leveraging the country’s abundant solar, wind, hydro, and biomass resources, coupled with supportive government policies, can drive the transition towards a cleaner and more resilient energy system.
By addressing challenges related to financing, grid integration, and regulatory frameworks, Nigeria can unlock investment opportunities, create jobs, and improve energy access. Collaboration with international organizations, technology transfer, and knowledge sharing can further accelerate the growth of the renewable energy sector in Nigeria. With a well-planned and coordinated approach, Nigeria can establish itself as a regional leader in renewable energy, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.

-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoVoIP Number: Everything You Need To Know
-

 Music3 weeks ago
Music3 weeks ago[Music] Gnash Ft Olivia O’Brien – I Hate you, I Love you
-

 Music2 weeks ago
Music2 weeks ago[INSTRUMENTAL] John Legend – All Of Me
-

 Music3 weeks ago
Music3 weeks agoAlan Walker – Faded [INSTRUMENTAL]
-

 Music3 weeks ago
Music3 weeks ago[Video] 21 Savage ft. Offset & Metro Boomin – Rap Saved Me
-

 Music3 weeks ago
Music3 weeks ago[Instrumental] Wiz Khalifa – See You Again ft. Charlie Puth
-

 ANE Stories3 months ago
ANE Stories3 months ago[STORY] AMAKA THE LESBIAN (Complete Episodes)
-

 Music3 weeks ago
Music3 weeks ago[Music] Akon – Sorry Blame It On Me